
This guide is intented for developers who wish to integrate a tag reader into to the Logical Reader API of the fosstrak ALE. The guide gives three examples to three existing Adaptors. In the second part a more detailed explanation about how to implement your own adaptor is given.
There are two different types of Logical Reader Definitions that should not be confused!
Dynamic Logical Reader Definitions are read by the fc-client and the fc-webclient. If you want to specify a logical reader at runtime through the Logical Reader API you need to use a Dynamic Logical Reader.
Static Logical Reader Definitions are read/written by the Logical Reader Manager upon ALE deployment. They contain additional information for the Logical Reader Manager.
The HALAdaptor provides an adaptor to the Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL).
Currently the HALAdaptor creates a SimulatorController object. This object in turn then sets up the HAL device as requested by the properties file.
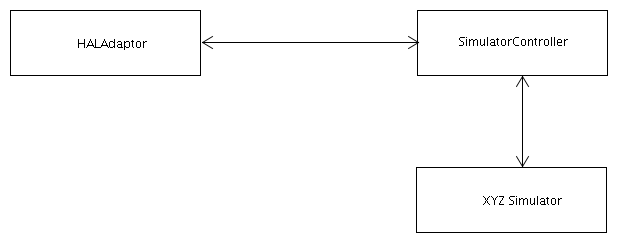
For example properties files refer to:
The HAL devices from the Fosstrak project currently do not provide a polling mechanism. To retrieve Tags from these devices we therefor need a mechanism to periodically poll the device. We chose an identifyThread that polls the HAL device in a regular time interval.
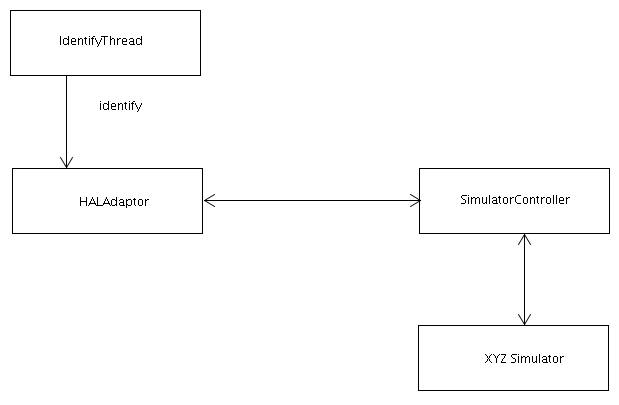
You need to provide all the following parameters to the HALAdaptor:
The xml definitions slightly differ for the dynamic and the static definition. Two full examples are given to illustrate where the parameters are defined.
If you want to load a HAL implementation not contained in the simulator framework (eg. impinj or feig implementation) you need to specify the corresponding implementation in the configuration file.
ATTENTION: Make sure that your implementation of the HardwareAbstraction interface provides a public constructor of the form XYZ(String halName, String configFile).
Example 1: for the impinj hal from fosstrak
// add the following property to the required properties
<property>
<name>ImplementingClass</name>
<value>org.fosstrak.hal.impl.impinj.ImpinjTCPIPController</value>
</property
Example 2: for the feig hal from fosstrak
// add the following property to the required properties
<property>
<name>ImplementingClass</name>
<value>org.fosstrak.hal.impl.feig.FeigTCPIPController</value>
</property>
Example 3: for the simulator controller (default)
// add the following property to the required properties
<property>
<name>ImplementingClass</name>
<value>org.fosstrak.hal.impl.sim.SimulatorController</value>
</property
Sample Configuration for a HALAdaptor
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<ns3:LRSpec xmlns:ns2="urn:epcglobal:ale:wsdl:1"
xmlns:ns3="urn:epcglobal:ale:xsd:1">
<isComposite>false</isComposite>
<readers/>
<properties>
<property>
<name>ReaderType</name>
<value>org.fosstrak.ale.server.readers.hal.HALAdaptor</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>Description</name>
<value>My first HAL device reader</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>PhysicalReaderName</name>
<value>MyReader1</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>ReadTimeInterval</name>
<value>1000</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>PropertiesFile</name>
<value>/props/SimulatorController.xml</value>
</property>
</properties>
</ns3:LRSpec>
In addition to the dynamic definition you must provide the reader name!
Sample Configuration for a HALAdaptor
<LogicalReader name="LogicalReader1">
<LRSpec isComposite="false"
readerType="org.fosstrak.ale.server.readers.hal.HALAdaptor">
<LRProperty name="Description"
value="HAL reader created during system startup"/>
<LRProperty name="AdaptorClass" value="HAL"/>
<LRProperty name="PhysicalReaderName" value="MyReader"/>
<LRProperty name="ReadTimeInterval" value="1000"/>
<LRProperty name="PropertiesFile"
value="/props/SimulatorController.xml"/>
<LRProperty name="ReadPoints" value="Shelf1,Shelf2"/>
</LRSpec>
</LogicalReader>
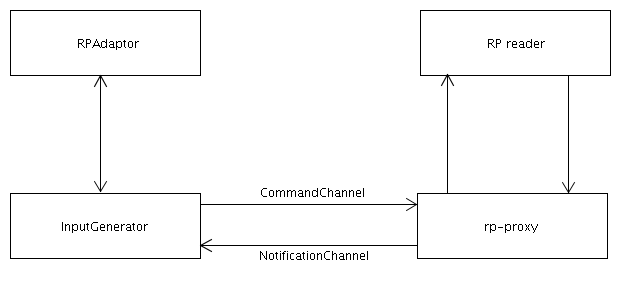
The RPAdaptor provides an adaptor to the reader protokoll (RP).
The RPAdaptor provides a default constructor and an initializer method. Both are called in the construction phase of the LogicalReader. The RPAdaptor implements all methods that are required by the logical reader API (basically these are the methods that are specified in LogicalReader and in BaseReader).
Aside the standard methods and fields the RPAdaptor requires some more functionality to communicate with a rp-proxy. The InputGenerator sets up the connection between the RPAdaptor and the rp-proxy. There are two channels that need to be created. The first one (command channel) is created for the communication from the RPAdaptor to the rp-proxy. The command channel uses the connection settings provided by ConnectionPoint. The second channel (notification channel) is used for the communication from the rp-proxy to the RPAdaptor and provides a channel for the delivery of tags from the physical reader. The settings provided by NotificationPoint are used to set up this channel. As soon as the RPAdaptor is started through the logical reader API the rp-proxy sends tag events that are then processed by the InputGenerator and sent through the RPAdaptor to the observers (CompositeReader or EventCycle).
The reader protocol provides a tag-smoothing by hardware. In the current implementation of the RPAdaptor we do not use this feature and poll the adaptor in a regular time intervall through a identifyThread instead. The main reason why we did without the tag smoothing is mainly an architectural decision. The reports generation performs this action in a higher application level again. To allow maximum flexibility in this high level tag smoothing we wanted to provide as many tags as possible.
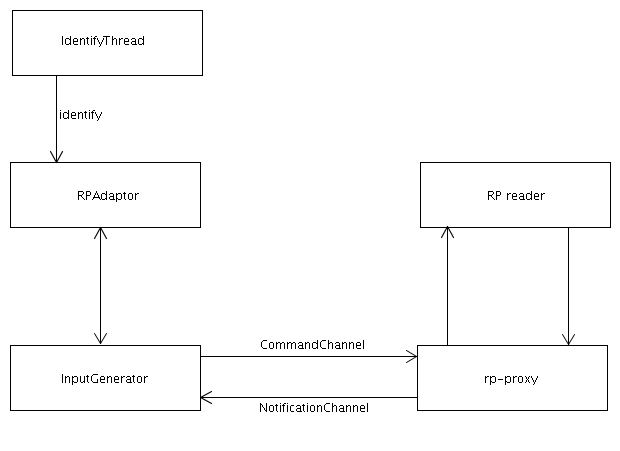
You need to provide all the following parameters to the RPAdaptor:
The xml definitions slightly differ for the dynamic and the static definition. Two full examples are given to illustrate where the parameters are defined.
Sample Configuration for a RPAdaptor
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<ns3:LRSpec xmlns:ns2="urn:epcglobal:ale:wsdl:1"
xmlns:ns3="urn:epcglobal:ale:xsd:1">
<isComposite>false</isComposite>
<readers/>
<properties>
<property>
<name>ReaderType</name>
<value>org.fosstrak.ale.server.readers.rp.RPAdaptor</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>Description</name>
<value>This Logical Reader consists of shelf 1
and shelf 2,3,4 of the physical
reader named MyReader</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>PhysicalReaderName</name>
<value>MyReader</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>ReadTimeInterval</name>
<value>1000</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>PhysicalReaderSource</name>
<value>Shelf1,Shelf2,Shelf3,Shelf4</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>NotificationPoint</name>
<value>http://localhost:9090</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>ConnectionPoint</name>
<value>http://localhost:8000</value>
</property>
</properties>
</ns3:LRSpec>
Sample Configuration for a RPAdaptor
<LogicalReader name="LogicalReader1">
<LRSpec isComposite="false"
readerType="org.fosstrak.ale.server.readers.rp.RPAdaptor">
<LRProperty name="Description" value="My physical Reader"/>
<LRProperty name="ConnectionPoint"
value="http://localhost:8000"/>
<LRProperty name="NotificationPoint"
value="http://localhost:9090"/>
<LRProperty name="ReadTimeInterval" value="200"/>
<LRProperty name="AdaptorClass" value="ReaderProtocol"/>
<LRProperty name="PhysicalReaderName" value="MyReader"/>
<LRProperty name="PhysicalReaderSource"
value="Shelf1,Shelf2,Shelf3,Shelf4"/>
</LRSpec>
</LogicalReader>
Fosstrak supports the integration of LLRP enabled readers through the Fosstrak LLRP Commander project. The LLRP Commander enables you to configure and manage your LLRP readers through a simple and intuitive eclipse GUI. For a detailed discussion how to use the Fosstrak LLRP Commander please refer to the respective project documentation website at Fosstrak.
For the integration of an LLRP enabled reader into the filtering and collection framework, Fosstrak implements a simple bridge to the reader management module of the Fosstrak LLRP Commander.
The following list shall give an overview to all available parameters that can be passed to filtering and collection through an LRSpec.
Sample Configuration for a LLRPAdaptor
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<ns3:LRSpec xmlns:ns2="urn:epcglobal:ale:wsdl:1" xmlns:ns3="urn:epcglobal:ale:xsd:1">
<isComposite>false</isComposite>
<readers/>
<properties>
<property>
<name>ReaderType</name>
<value>org.fosstrak.ale.server.readers.llrp.LLRPAdaptor</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>Description</name>
<value>my llrp reader</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>PhysicalReaderName</name>
<value>ethzReader</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>ip</name>
<value>127.0.0.1</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>port</name>
<value>5084</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>clientInitiated</name>
<value>true</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>antennaID</name>
<value>1,2</value>
</property>
</properties>
</ns3:LRSpec>
Sample Configuration for a LLRPAdaptor
<LogicalReader name="LogicalReader1">
<LRSpec isComposite="false"
readerType="org.fosstrak.ale.server.readers.llrp.LLRPAdaptor">
<LRProperty name="Description" value="my llrp reader"/>
<LRProperty name="PhysicalReaderName"
value="ethzReader"/>
<LRProperty name="ip"
value="127.0.0.1"/>
<LRProperty name="port" value="5084"/>
<LRProperty name="clientInitiated" value="true"/>
<LRProperty name="antennaID" value="1,2"/>
</LRSpec>
</LogicalReader>
For testing purposes the TestAdaptor can be used. The TestAdaptor simulates a reader that from time to time reads a tag.
As the TestAdaptor is not intended to be used as a productive reader adaptor only the basic configuration parameters will be explained here.
Sample Configuration for a RPAdaptor
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<ns3:LRSpec xmlns:ns2="urn:epcglobal:ale:wsdl:1"
xmlns:ns3="urn:epcglobal:ale:xsd:1">
<isComposite>false</isComposite>
<readers/>
<properties>
<property>
<name>ReaderType</name>
<value>org.fosstrak.ale.server.readers.test.TestAdaptor</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>Description</name>
<value>Test Adaptor to test performance</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>tps</name>
<value>1000</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>gain</name>
<value>0</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>wt</name>
<value>5000</value>
</property>
</properties>
</ns3:LRSpec>
Sample Configuration for a RPAdaptor
<LogicalReader name="LogicalReader1">
<LRSpec isComposite="false"
readerType="org.fosstrak.ale.server.readers.test.TestAdaptor">
<LRProperty name="Description"
value="Test Adaptor to test performance"/>
<LRProperty name="tps" value="100"/>
<LRProperty name="wt" value="3000"/>
<LRProperty name="gain" value="0"/>
</LRSpec>
</LogicalReader>
When you want to integrate your own reader into the logical reader API there are only few restrictions and obligations you need to obey.
In a first step you should create a new package for your reader adaptor.
Create a new class with the name of your adaptor and let this class extend the class BaseReader.
You need to overwrite the following methods
Pay attention to flag the state of your adaptor correctly through the methods (setConnected, setStarted, ...)
Instead of a constructor with arguments we chose the approach of an default constructor and an initializer method. To ensure that your adaptor is setup correctly implement the constructor and the initizalizer method as following:
pay attention to put the call to the initializer method of the superclass ("super.initialize(name, spec)"). After that feel free to express yourself.
Now you are ready to use your reader in the logical reader API.
sample code of an empty reader adaptor:
package org.fosstrak.ale.server.readers.myreader;
import org.fosstrak.ale.server.Tag;
import org.fosstrak.ale.server.readers.BaseReader;
import org.fosstrak.ale.server.readers.LRSpec;
import org.fosstrak.ale.wsdl.ale.epcglobal.ImplementationException;
import org.fosstrak.reader.hal.HardwareException;
import org.fosstrak.reader.hal.Observation;
public class MyReaderAdaptor extends BaseReader {
public MyReaderAdaptor() {
super();
}
public void initialize(String name, LRSpec spec)
throws ImplementationException {
super.initialize(name, spec);
}
@Override
public void addTag(Tag tag) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
@Override
public void connectReader() throws ImplementationException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
@Override
public void disconnectReader() throws ImplementationException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
@Override
public Observation[] identify(String[] readPointNames)
throws HardwareException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
@Override
public void start() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
@Override
public void stop() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
@Override
public void update(LRSpec spec) throws ImplementationException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
}