
The Reader-interface provides access to the physical LLRP reader. It maintains the connection, handles errors, delivers and retrieves LLRP messages.
In the following guide the implementation of the reader interface ReaderImpl is discussed and used as a reference.
public void connect(boolean clientInitiatedConnection)
throws LLRPRuntimeException, RemoteException;
There are two different types of connections that can be used for the communication between the physical reader and the logical reader:
The user can specify the desired connection profile during the connection setup by specifying the boolean clientInitiatedConnection. If set to true the first connection model is selected (the logical reader connects to the physical reader). If set to false the second model is chosen.
Note:If you create the reader through the adaptor interface (recommended) and if you specified connectionImmediately you will not have to call the connect method as the adaptor will take care of this for you.
As soon as the connection to the physical reader is established a connection watchdog is installed. This watchdog instructs the LLRP reader to periodically send a KEEP_ALIVE message. If this message is not received for a certain time interval, the connection is assumed to be dead. The reader then removes all connection profiles and triggers an exception.
public void disconnect() throws RemoteException;
The client closes the LLRP connection.
public void send(byte[] message) throws RemoteException;
The reader checks the message for validity (correct encoding, valid LLRP message...). Then the message is sent to the physical reader. When an unknown exception is triggered the reader usually disconnects.
Remark: We advise you to use the adaptor management to enqueue messages instead of this sending facility. The reason is that a sending through this method is blocking (synchronous) whereas the sending through the adaptor management is (non-blocking) asynchronous.
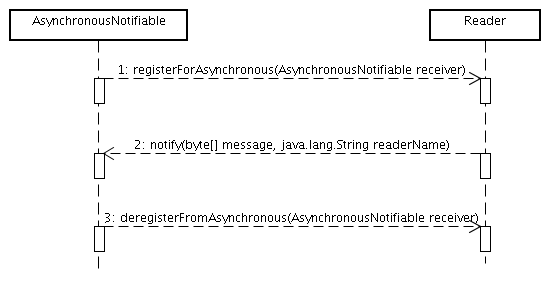
Readers support a asynchronous callback mechanism for exceptions and for incoming LLRP messages. Before you can use the asynchronous reporting facility you need to register the interface AsynchronousNotifiable on the reader. Whenever an exception occurs or when a LLRP message arrives the notifier will be updated and be provided with the message/exception.
Notice: When you create an reader through the adaptor management this callback mechanism is already setup for you and you will not need to perform any additional steps.
The registering and deregistering can be done with the following methods:
// registering
public void registerForAsynchronous(AsynchronousNotifiable receiver)
throws RemoteException;
// deregistering
public void deregisterFromAsynchronous(AsynchronousNotifiable receiver)
throws RemoteException;
The following graphic shall give you an overview to the mechanism of the asynchronous callback mechanism.
Whenever an error occurs on the reader the error callback is invoked. As the reader uses ltk to send/receive messages the error callback is slightly different to the one in the adaptors.
public void errorOccured(String message) {
throws RemoteException;
Basically this corresponds to a observer-Pattern. The observable (in this case the reader) notifies all the observers (in this case all the registered asynchronous notifiables). The observable triggers the method notifyError.
Whenever an LLRP message arrived from on the reader, the message callback is invoked. For the same reason as with the error callback also the message reporting callback is slightly different to the one in the adaptor.
public void messageReceived(LLRPMessage message);
As with the error callback this is comparable to the observer- pattern. The observable triggers the method notify on all the observers.
The standard configuration of the reader is not to report the KEEP_ALIVE messages (they occur very often!). However you can instruct the reader to report also those messages.
The Reader-class exports a simple interface to register for asynchronous message notification. If one is interested into all incoming LLRP messages, one can register a callback through the method void registerForAsynchronous(AsynchronousNotifiable receiver). As soon as an LLRP message arrives on the reader the method void notify(byte[] message, java.lang.String readerName) is invoked. In case of an error the error message is reported through the method void notifyError(LLRPRuntimeException e, java.lang.String readerName).
